|

WHERE ARE THEY USED?
SHAPEMATE* IB is used on the outisde surfaces of walls
by bounding and dabbling. The boards are produced with
rugged front surfaces to increase the paste power for
applications from outside. On the back surfaces along
its height it is grooved at 5 cm intervals with a size
of 5x5 mm. To enable perfect pasting.




HOW ARE THEY APPLIED?
- For the
external insulation, the boards are pasted to the
external face of the wall using cement based pastry
mortar without solvent content. (If on the back face
there is some kind of painting etc. that is preventing
ease of pasting, the surface is to be abrades and thus
prepared for pasting).
- The pastry
mortar is left drying for a while and the boards are
fixed to the surface at the back in rows of 6 for every
m2 using plastic nail insulation dabbles. (The dabbling
process is very important and if the back face is not
right for the process a rough plastering of 2 cm.
Thickness is to be provided).
- Cement based
plaster with added latex is applied directly onto the
surface of the boards in thickness of a few mms. Alkali
proof glass fleece plaster rigger filet is pasted onto
the plaster surface (before it is dried) using steel
trowel. And later a few mm. Of plaster is applied and
then left for drying. The most important matter in this
process is that the plaster rigger fillet is placed in
the middle of total external plaster layer or close to
its external face.
- Putting a
final layer of cover, which is decorative without any
solvent content and has a surface layer, which is rugged
but windy, completes the application process.
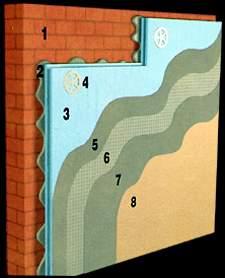
1)
External side of the walls
2) Adhesive mortar
3) Shapemate* IB thermal
resistance board
4) Dabble
5) Plaster (min. 2 mm.)
6) Fibermesh
7) Pasting plaster (min. 2
mm.)
8) Plaster |
ADVANTAGES
-
Shapemate IB thermal resistance boards can be used for
the roof of cellars, bottoms of porch balconies etc, and
for both columns and beams by putting into moulds as
well as by applying plasters later and eliminates heat
bridges due to its high thermal resistance capacity.
-
The rugged surfaces of the boards tightly grab the
surface where it is pasted to and also the plaster it is
pasted to remains strong for the length of life of the
building and keeps its thermal resistance qualities.
-
External insulation protects the external shell of the
building against differences in temperatures and thus
against wear.
-
Applications for external insulation prevent dampness by
allowing condensation to occur on the external face of
the building and establish a healthy living quarter.
-
Applications external insulation eliminates the change
of air movement due to the temperature of the wall
internal surface being close to ambient temperature and
fixed at the ambient temperature. Also prevents erosion
of the surface layer, split of the paint and plaster.
-
Shapemate IB thermal resistance boards do not require
renewal work to be carried out very often and keep their
thermal resistance characteristics for the length of the
life of the building.
-
Allows smaller and more economical use of devices for
heating and cooling. Economizes on maintenance and
operational work.
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE MATERIALS OF SHAPEMATE IB FOR
EXTERNAL WALL INSULATION
MATERIALS FOR THERMAL
RESISTANCE (TS 11989 compatible TSE standards). For
the application external wall insulation cap less porous
polystyrene - extruded foam XPS boards used must
definitely have rugged and/or grooved surfaces (TSE 825
standards, article number 10.2.1.2.1. of attachment
number 5 of the official gazette numbered and dated
23725 and June 14, 1999). In the case of surfaces being
armored the paste resistance of the boards between paste
mortar and plaster shall not be sufficient. (For this
reason for the products having grooved and rugged
surfaces test results carried out according to TS 11989
by TSE must be obtained from the manufacturers).
RATE OF THERMAL
CONDUCTIVITY (LAMDA). It must not be larger than
0.031 W/m.K for aging at 10 C for 90 days. (For boards
with both of the surfaces being rugged test results
carried out at the laboratories of TSE must definitely
be obtained from the manufacturer).
DENSITY. Must not
be at lower than 25 kg/m3 density. Although under TS
825, article number 10.2.1.2.1 of attachment number 5
the lower limit of density is given as 20 kg/m3 for the
boards with rugged surfaces we propose values of 27-28
kg/m3 density to be used to be able to reach the value
of 0.031 W/m.K.
SIZE DETERMINATION
a) Change of dimensions in the length and the width must
be zero at 60 C and 90 % relative humidity.
b) Change in dimensions must not exceed 2 % under 20-kPa
stresses and at a temperature of 80 C.
c) Must not exceed 2 % under 40-kPa stresses and at a
temperature of 70 C.
Size determination is one of the most important factors
especially for the wall applications. Size changes
occurring due to differences in temperatures might
create problems on the frontal surfaces. The sizes of
the cells, their placements and their balances in three
directions are very important regarding paste resistance
and size dimension involved.
WATER ABSORBTION.
The water absorption rate for prolonged periods using
full dipping method must not exceed 0.5 % in volume.
Otherwise, the thermal resistance material absorbs the
water of the paste mortar or pasting plaster it is in
contact with and changes the rate of thermal
conductivity (lambda) and the building will start to
consume more energy than anticipated at the beginning.
In addition, as the result of freeze thaw circle of the
absorbed water cracks might occur in the plaster.
THE PASTING RESISTANCE
TO THE PLASTER. The pasting resistance of the
thermal resistance boards to paste plaster must not be
lower than 80 kPa. The preferred rates are larger than
100 kPa.
WATER VAPOUR DIFFUSION
RESISTANCE. It must be between 90 and 110. The
values must remain at these levels so that no
condensation occurs at the wall cross-sections and at
the same time the building can take wind. However, a
test for condensation at the wall cross sections must be
carried out under any circumstances (please refer to TS
825 standards given in the official gazette numbered and
dated 23725 and June 14, 1999).
PRESSURE RESISTANCE.
Must not be lower than 200 kPa (TSE 11989, class C2).
RESISTANCE TO FIRE.
Must pass the B2 test first, then must be proven that it
has passed B1 class by applying furnace tests and that
it has not been dripping. Besides the documents obtained
from TSE there must also be certificates granted by the
test institutes in Germany.
CAPILARITY. Must
be zero.
SPECIFICATIONS OF THE
SURFACE. For the application of thin layer pasting,
the external surfaces where plaster is applied must only
be rugged (not grooved), the back face pasted to the
wall must be rugged as well as grooved. Thus, better
pasting to the back face shall have been obtained and a
relatively more homogenate plaster surface would have
been obtained on the external side.
LENGTH, WIDTH,
DEVIATION FROM THE SET SQUARE, SURFACE PLANE, THICKNESS.
Must be in conformity of TS 11989.
SIDE PROFILES. The
long sides being tongued would prevent the work of heat
bridges.
* Trademark of Dow
Chemical Company.
|