|

WHERE ARE THEY USED?
Roofmate* SL is the ideal thermal insulation material of
the flat roofs thermal resistance roofs which is
suitable for walking on or not or greenhouse type flat
roofs.

HOW ARE THEY APPLIED?
- After the
application of the slope cement, the drainer and water
proof membrane, both water impermeability and drainage
tests have to be carried out.
- The Roofmate
SL boards are placed freely on the water proof membrane
system. Care must be given to put the sides of the
boards on top of each other, in full line and that the
boards do not fly off in stormy weather conditions.
- A filter
layer (felted cloth, geotextile) is laid out on the
boards and materials like sand etc. Are thus prevented
from flowing down the water and board joints.
- Gravel of 5
cm. Thickness (Æ16-32 mm.) is
laid on the flat roofs, which is not suitable for
walking on. On the flat roofs where people can walk on
thin layer of gravel is laid on top of the filter layer.
The boards are laid on this gravel without using mortar
and the detailed work is then completed. Or, without
using a filter layer and gravel the boards are placed on
top of the Roofmate SL boards with the use of plastic
filler blocks. Both of the details allow ease of use for
maintenance purposes.
- It is
possible to fix the boards on the felted cloth and on
the layer of thin (Æ 4-8 mm.)
gravel of 2-3 cm. Thickness and to use covers like
mosaic or alum. However, it is preferred that the cover
layer allows the flow of vapor.
- For
greenhouse roofs a repeated filter layer and vegetation
earth is laid on top of the gravel layer.
- The drainers
to be used must be set to draw any water from all layers
and their numbers and capacity must be able to drain
water at a fast speed.
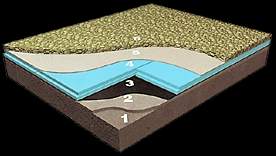
1) Floor cement
2) Slope cement
3) Water proofing membrane
4) Roofmate * SL thermal
insulation board
5) Separator layer (felted cloth,
geotextile etc.)
6) Gravel (Æ
16-32 mm., min. 5 cm.)
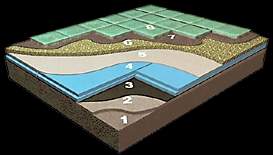
1) Floor cement
2) Slope cement
3) Water proofing membrane
4) Roofmate * SL thermal
insulation board
5) Separator layer (felted cloth,
geotextile etc.)
6) Gravel (Æ
4-7 mm., min. 2 cm.)
7) Mortar
8) Board covering
ADVANTAGES
- At the traditional application of flat roofing
systems the thermal insulation material is protected
from water by using water insulation at top and bottom
barriers. However, in this situation the water proof
membrane are quickly worn out due to the differences in
temperatures and the effects of mechanical influences,
thus loosing its thermal insulation specifics and
requires very expensive maintenance and renewal work. In
addition, it requires very high quality materials and
workmanship and it is not compatible with the physical
specifications of the building itself.
- For the inverted roofing system
the water proofing membrane are protected from effects
mentioned above with the help of Roofmate SL boards.
Also, it doesn't require use of vapor barriers and
protection cement, with less cost, its application is
simple and fast, can be applied under every weather
condition.
- It can
be uninstalled easily to check on the status of water
proof membrane; after maintenance work is carried out it
can be reinstalled without any loss of material and
quality. Hence, costs related to maintenance and repair
is kept at lowest levels.
- The Roofmate SL boards have a
minimum pressure resistance of 30 tons/m2 and stretch
resistance of 2 %.
- The boards are snow and frost
proof, is highly resistant to frost-thaw circle.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE MATERIALS OF ROOFMATE
SL FLAT ROOFING SOLUTIONS
MATERIALS FOR THERMAL RESISTANCE (TS 11989
compatible TSE standards). For the application of
terrace roofing systems the cap less porous polystyrene
- extruded foam XPS boards used must definitely have
armored (binded) surfaces (TSE 825 standards, article
number 10.2.1.2.2. of attachment number 5 of the
official gazette numbered and dated 23725 and June 14,
1999). In the case of surfaces being curse the use of
the boards on the reversed roofing systems is not
appropriate regarding the values of thermal conductivity
(lambda), water absorption, frost thawing.
RATE
OF THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY (LAMDA). It must not be
larger than 0.027 W/m.K. After aging at 10 C for 90
days.
DENSITY. Must not be at lower than 32 kg/m3 density.
Although under TS 825, article number 10.2.1.2.2 of
attachment number 5 the lower limit of density is given
as 30 kg/m3 for the boards with armored (binding)
surfaces we propose values of 32 kg/m3 and higher to be
used.
PRESSURE RESISTANCE. Must not be lower than 300 kPa
(TSE 11989, class C3).
STRECH
RESISTANCE. It must not be lower than 110 kPa. (This
value can be defined as the load at its maximum, which
the material can carry for 50 years on a continuous
basis under a deformation of up to 2 %. Also, as the
load for statistical calculations 110 kPa should be
taken as basis instead of 300 kPa).
WATER ABSORBTION. The water absorption rate for
prolonged periods using full dipping method must not
exceed 0.2 % in volume.
WATER
ABSORBTION WITH DIFFUSION OVER LONG PERIODS. The
rate of water absorption with diffusion over long
periods must not exceed 1 % in volume.
FROST
THAW. The rate of water absorption using freeze thaw
method must not exceed 0.2 % in volume. Also, the
reduction in pressure resistance as the result of freeze
thaw test must not exceed 2 % (the rate of 10 % as the
standard is the upper limit).
WATER
VAPOUR DIFFUSION RESISTANCE. It must be between 100
and 200.
SIZE
DETERMINATION
a) Change of dimensions in the length and the width must
be zero at 60 C and 90 % relative humidity.
b) Change in dimensions must not exceed 2 % under 20-kPa
stresses and at a temperature of 80 C.
c) Must not exceed 2 % under 40-kPa stresses and at a
temperature of 70 C.
RESISTANCE TO FIRE. Must pass the B2 test first,
then must be proven that it has passed B1 class by
applying chimney furnace tests and that it has not been
dripping. Besides the documents obtained from TSE there
must also be certificates granted by the test institutes
in Germany.
CAPILARITY. Must be zero.
SPECIFICATIONS OF THE SURFACE. Must be armored
(binding).
LENGTH, WIDTH, DEVIATION FROM THE SET SQUARE, SURFACE
PLAIN, THICKNESS. Must be in conformity of TS 11989.
SIDE
PROFILES. Tongue grooved side profiles would prevent
the work of heat bridges.
STRETCH RESISTANCE. Must not be lower than 110 kPa
at the applications on the beam rafter without roof
wood. Otherwise, people would not be able to walk on it.
Even at these values the thickness of the board and the
gaps left between beams rafters must not exceed the
values given by the manufacturers.
* Trademark of Dow
Chemical Company.
|