|

WHERE ARE THEY USED?
They are used for the base floors, wooden flooring, and
systems with heating from the floor, the floors
separating the floors, in short for all the flooring
where heat loss can be anticipated.
HOW ARE THEY USED?
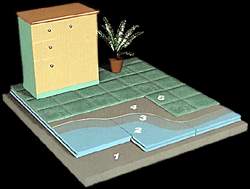
-
Directly onto the concrete floor and without
leaving any space or gap.
-
If a mortared floor lining is to be applied on
it, polyethylene layer is laid on top of it as a
separating layer and if required, a thin layer of alum
is spread and mortared lining is applied. For carpeted,
PVC wooden parquet linings etc. pasting or lathed
fixation is applied on the layer of alum.
-
For the heated floors the boards are laid on top
of the floor concrete. After a polyethylene folio as
separating layer is laid, the heating pipes are placed
using plastic legs and an alum layer of appropriate
thickness is applied and care is taken so that the
heating pipes remain in the middle of the thickness of
the alum. After that the detail is completed with the
floor lining.
1) Floor
cement
2) Floormate* 200 thermal
insulation board
3) Separation layer,
poly-ethylene folio
4) Heating pipes
5) Alum
6) Floor covering materials
(parquet etc.)
|
 |
1) Floor
cement
2) Floormate* 200 thermal
insulation board
3) Separation layer,
poly-ethylene folio
4) Mortar
5) Floor covering or alum
layer
|
 |
ADVANTAGES
- Floormate* 200 possesses high
resistance qualities against pressure loads and
stretching over time. For that reason, it doesn't cause
wear out with the materials used for lining.
- Since the pressure resistance
is high it reduces cost for linings of the type similar
to mosaics.
- The water repent ionic quality
of the product enables protection of the specifications
relating to thermal resistance for possible incidents
and prevention of occurrence of damage likely to happen
over time especially for applications of structural
insulation, heating and cold storage houses.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR
THE MATERIALS OF THE FLOORMATE 200 OFFICE AND
RESIDENTIAL BUILDING FLOORING INSULATION
MATERIALS FOR THERMAL RESISTANCE (TS 11989
compatible TSE standards). The cap less porous
polystyrene - extruded foam XPS boards used for the
flooring of offices and residential buildings must
definitely have armored (binded) surfaces (TSE 825
standards, article number 10.2.1.2.2. of attachment
number 5 of the official gazette numbered and dated
23725 and June 14, 1999).
RATE
OF THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY (LAMDA). It must not be
larger than 0.028 W/m.K after aging at 10 C for 90 days.
DENSITY. Must not be at lower than 30 kg/m3 density.
Under TS 825, article number 10.2.1.2.2 of attachment
number 5 the lower limit of density is clearly given as
30 kg/m3 for the boards with armored (binding) surfaces.
PRESSURE RESISTANCE. Must not be lower than 200 kPa
(TSE 11989, class C3).
STRECH
RESISTANCE. It must not be lower than 80 kPa. (This
value can be defined as the load at its maximum, which
the material can carry for 50 years on a continuous
basis under a deformation of up to 2 %. Also, as the
load for statically calculations 80 kPa should be taken
as basis instead of 200 kPa).
WATER
ABSORBTION. The water absorption rate for prolonged
periods using full dipping method must not exceed 0.2 %
in volume.
WATER
VAPOUR DIFFUSION RESISTANCE. It must be in between
100 and 200.
SIZE DETERMINATION
a) Change of dimensions in the length and the width must
be zero at 60 C and 90 % relative humidity.
b) Change in dimensions must not exceed 2 % under 20-kPa
stresses and at a temperature of 80 C.
c) Must not exceed 2 % under 40-kPa stresses and at a
temperature of 70 C.
RESISTANCE TO FIRE. Must pass the B2 test first,
then must be proven that it has passed B1 class by
applying furnace tests and that it has not been
dripping. Besides the documents obtained from TSE there
must also be certificates granted by the test institutes
in Germany.
CAPILARITY. Must be zero.
SPECIFICATIONS OF THE SURFACE. Must be armored
(binding).
LENGTH, WIDTH, DEVIATION FROM THE SET SQUARE, SURFACE
PLAIN, THICKNESS. Must be in conformity of the
tolerances under the TS 11989 standards.
SIDE
PROFILES. tongued side profiles would prevent the
work of heat bridges.
* Trademark of Dow
Chemical Company.
|